Raft in breif
概览

安全性保证
Raft保证以下五条准则在算法运行期间始终成立(Invariance):
Election Safety: 一个世代term内至多产生一个leader.Leader Append-Only: leader在自己的日志中只会追加新Entry而不会去修改或删除某一项Entry.Log Matching: 若俩日志中某Entry有着相同的index和term, 则该Entry之前的日志项都相同.Leader Completeness: 若一个Entry在某世代term内已committed, 则此后任何term内该Entry都存在.State Machine Safety: 若状态机应用了某Entry, 则该index处不应再应用其他Entry.
Leader选举

选举Leader思想很简单: 某个节点开始竞选某个世代term的leader, 向其他节点发送RequestVote RPC, 如果他得到的支持票数满足quorum机制, 则成为该term内合法的leader. 这里面的关键问题是如何防止出现split brain问题(确保每个term内仅会出现一个leader).
首先, 对于一个给定的Term, 服务器只会进行一次投票(且只会投给Term更高的), 且为了避免出现过多的竞选者, 各节点的触发选举超时时间应随机化. 此外, RequestVoteRPC里还应带上候选者的日志信息, 避免选出落后的Leader而导致日志覆盖(违背线性化).
日志复制
要点:
大部分节点(
quorum)已知晓的Entry的状态即为已committed, Leader会将其应用到状态机(持久化),返回客户端执行结果.Leader在下一次的
AppendEntries RPC中带上commitedIndex,这样followers就知道自己相应的日志项也该应用到状态机了.Leader在
AppendEntries RPC中带上新Entry之前的Entry信息,follower若检查到自己没有该Entry的话,就会知道自己之前的复制可能出了差错并拒绝掉该Entry. 只要follower的结果返回了成功, 我们就知道该follower与leader至少在新Entry之前是保持一致了的.Leader宕机带来的不一致问题(复制以Leader为准则): Leader通过
AppendEntries RPC不断来回的试探到follower与之匹配的日志记录, 然后将其覆盖重写为与自己一致的项.新Leader产生后, 可以先复制一个
no-op Command的Entry从而更快的获得各follower的复制进度. 对前任的遗留日志需通过提交自己任期的日志去进行间接提交. 原因如下:
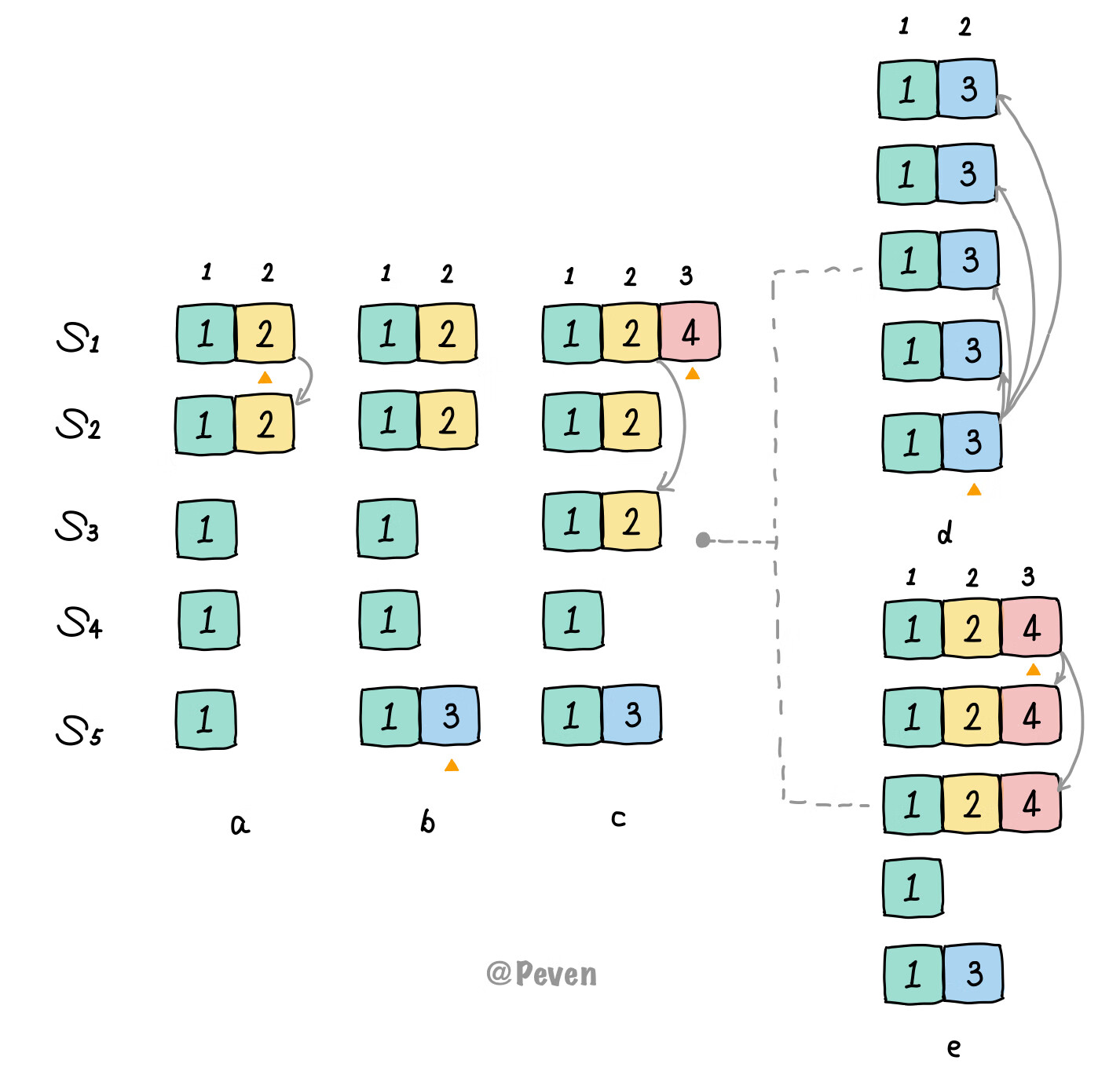
a: 此时$S_1$成为term 2的leader并产生了Entry, 只复制到了$S_2$后就crash了;b: $S_5$成为term 3的leader并产生了Entry, 但还没复制就crash了;c: $S_1$成为term 4的leader并产生了Entry, 他先复制前任的遗留Entry到了大多数节点, 但还没持久化提交就又crash了;d: $S_5$成为新term的leader, 未产生Entry, 接着它复制前任遗留的Entry, 并导致了日志重写.
可以看到, 由于策略是上来就提交前任的遗留Entry, 导致了日志被重写. 正确做法的结果应如e: c时刻$S_1$成为leader后, 等待到提交自己任期的Entry, 前任的遗留日志自然会被复制从而被间接提交. 且此后$S_5$由于落后的日志也不会再成功竞选.
成员(配置)变更
变更配置时, 可不是简单的直接从旧的配置换到新的上去就行(换配置然后重启). 为保证系统可用性和安全性, 应使用2-phase:
- 第一步: 禁止旧配置的系统继续接受新的请求
- 第二步: 切换到新的配置文件上
在新旧配置转换过渡期间会同时存在两种配置, 这期间系统可能会产生split brain. Raft采用的2-phase机制叫joint consensus: 其使得即使在过渡期间系统仍能正确的, 安全的运行: 如在$C_{old}$到$C_{new}$的过渡期: $C_{old, new}$ , 为防止split brain, 决议要同时通过两个配置的joint集合的quorum通过才行.
思考如下的配置拓扑:
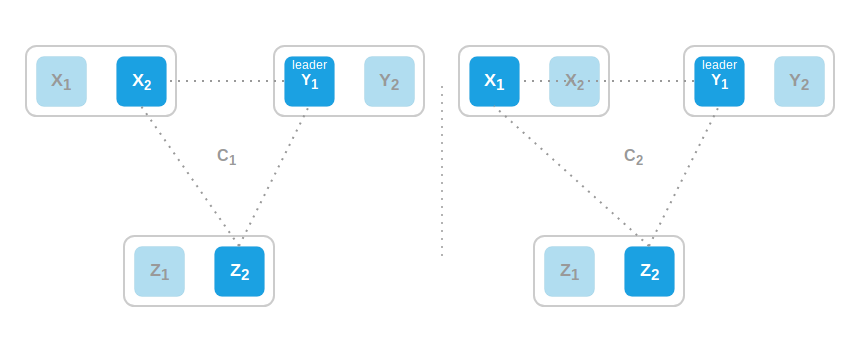
如上图, 3个region(X, Y, Z)中配置$C_1$($X_2$, $Y_1$, $Z_1$) 组成的raft集群($Y_1$是leader)现在想要切换到配置$C_2$(新增$X_1$, 移除$X_2$). 先看看直接切换:

可以看到, $Y_1$收到confchange后并切换到$C_2$, 与$X_1$组成了$C_2$的quorum, 与此同时, $X_2$与$Z_2$也组成了$C_1$的quorum, 这就导致了split brain. 而其中的原因是我们太过贪心, 将$X_1$的加入和$X_2$的移除同时进行了.
所以接下来我们先增加$X_1$, 再移除$X_2$(1 by 1, 让大部分节点知晓到第一次变更后再处理下一条). 则先$C_2$ = ($X_1$, $X_2$, $Y_1$, $Z_2$), 其quorum为3, 此时先变更的$X_1$与$Y_1$一起并无法做出决议. 但这样就真的完美解决了我们的问题吗?
若这时region X整个不可达时, 整个集群就得等待其重新上线才能恢复服务. 这时就引出了joint consensus:
针对上例, 我们在进行配置变更时, 引入过渡期配置$C_{1,2}$ = $C_1$ && $C_2$ = ($X_2$, $Y_1$, $Z_2$) && ($X_1$, $Y_1$, $Z_2$) , 过渡期间任何决议都得同时通过两个配置中的quorum通过才行:
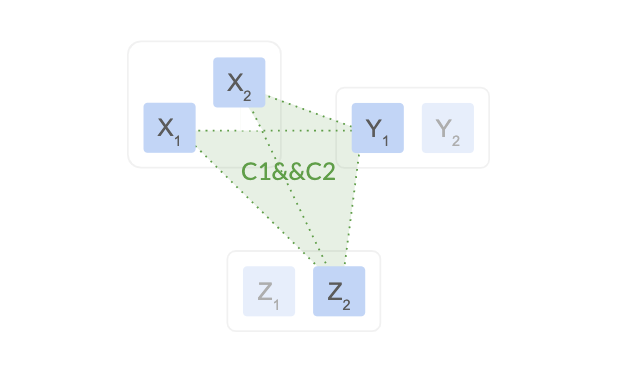
这样, 即使X region整个失联, 集群仍是能够正常的运行.
使用joint consensus进行成员配置变更的大致流程如下:
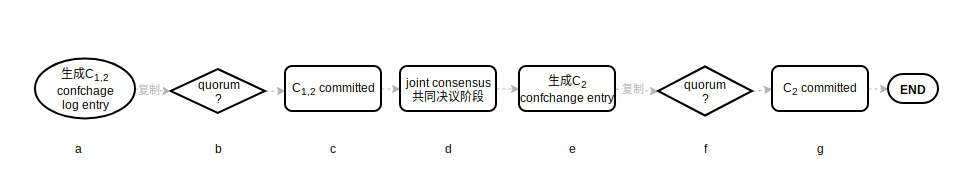
其中, 需要注意的问题是如果leader发生crash了会怎样? 由于有Leader completeness的保证, 在$C_{1,2}$ committed后, crash后新的leader的配置也一定会是$C_{1,2}$. 还有一种情况: $C_2$ committed后, leader可能并不在此配置中, 此时leader自己降级为follower, 进行$C_2$配置内的选举.
此外, Raft还针对新增的成员引入了一个新的角色: learner(可以看看这篇文章: etcd learner design). 在节点加入集群初期, 由于日志复制状态通常会远远落后于leader, learner在日志追赶未完成前不会参与决议投票. 而对于已移除(不在新配置中)但未下线的节点, 其在心跳超时后会发起RequestVote RPC反复干扰现有配置的集群, 避免的方式为只要节点认为现有leader还在(最小选举超时机制),就不理会新的RequestVote RPC.
日志压缩
我们不能允许日志记录无休止的增长, 必须对其进行压缩以使获得更小的空间占用和更高效的日志复制:
通过check point处的快照(Snapshot)记录保留committed entries的最新状态, 旧的日志条目就可以删除掉.

参考Etcd raft库的设计: 该库将raftLog分为storage(stable)和unstable.
Snapshot定义:
1message SnapshotMetadata {
2 optional ConfState conf_state = 1 [(gogoproto.nullable) = false];
3 optional uint64 index = 2 [(gogoproto.nullable) = false];
4 optional uint64 term = 3 [(gogoproto.nullable) = false];
5}
6
7message Snapshot {
8 optional bytes data = 1;
9 optional SnapshotMetadata metadata = 2 [(gogoproto.nullable) = false];
10}
storage.go:
1type Storage interface {
2 // TODO(tbg): split this into two interfaces, LogStorage and StateStorage.
3 // InitialState returns the saved HardState and ConfState information.
4 InitialState() (pb.HardState, pb.ConfState, error)
5 // Entries returns a slice of log entries in the range [lo,hi).
6 // MaxSize limits the total size of the log entries returned, but
7 // Entries returns at least one entry if any.
8 Entries(lo, hi, maxSize uint64) ([]pb.Entry, error)
9 // Term returns the term of entry i, which must be in the range
10 // [FirstIndex()-1, LastIndex()]. The term of the entry before
11 // FirstIndex is retained for matching purposes even though the
12 // rest of that entry may not be available.
13 Term(i uint64) (uint64, error)
14 // LastIndex returns the index of the last entry in the log.
15 LastIndex() (uint64, error)
16 // FirstIndex returns the index of the first log entry that is
17 // possibly available via Entries (older entries have been incorporated
18 // into the latest Snapshot; if storage only contains the dummy entry the
19 // first log entry is not available).
20 FirstIndex() (uint64, error)
21 // Snapshot returns the most recent snapshot.
22 // If snapshot is temporarily unavailable, it should return ErrSnapshotTemporarilyUnavailable,
23 // so raft state machine could know that Storage needs some time to prepare
24 // snapshot and call Snapshot later.
25 Snapshot() (pb.Snapshot, error)
26}
27
28// MemoryStorage implements the Storage interface backed by an
29// in-memory array.
30type MemoryStorage struct {
31 // Protects access to all fields. Most methods of MemoryStorage are
32 // run on the raft goroutine, but Append() is run on an application
33 // goroutine.
34 sync.Mutex
35 hardState pb.HardState
36 snapshot pb.Snapshot
37 // ents[i] has raft log position i+snapshot.Metadata.Index
38 ents []pb.Entry
39}
log.go:
1type raftLog struct {
2 // storage contains all stable entries since the last snapshot.
3 storage Storage
4 // unstable contains all unstable entries and snapshot.
5 // they will be saved into storage.
6 unstable unstable
7 // committed is the highest log position that is known to be in
8 // stable storage on a quorum of nodes.
9 committed uint64
10 // applied is the highest log position that the application has
11 // been instructed to apply to its state machine.
12 // Invariant: applied <= committed
13 applied uint64
14 logger Logger
15 // maxNextEntsSize is the maximum number aggregate byte size of the messages
16 // returned from calls to nextEnts.
17 maxNextEntsSize uint64
18}
log_unstable.go:
1// unstable.entries[i] has raft log position i+unstable.offset.
2// Note that unstable.offset may be less than the highest log
3// position in storage; this means that the next write to storage
4// might need to truncate the log before persisting unstable.entries.
5type unstable struct {
6 // the incoming unstable snapshot, if any.
7 snapshot *pb.Snapshot
8 // all entries that have not yet been written to storage.
9 entries []pb.Entry
10 offset uint64
11 logger Logger
12}
用一张图来直观的展示:

See Also
Raft Paper: https://raft.github.io/raft.pdf
Etcd Raft lib: https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd/tree/main/raft
Availability and Region Failure: Joint Consensus in CockroachDB: https://www.cockroachlabs.com/blog/joint-consensus-raft
